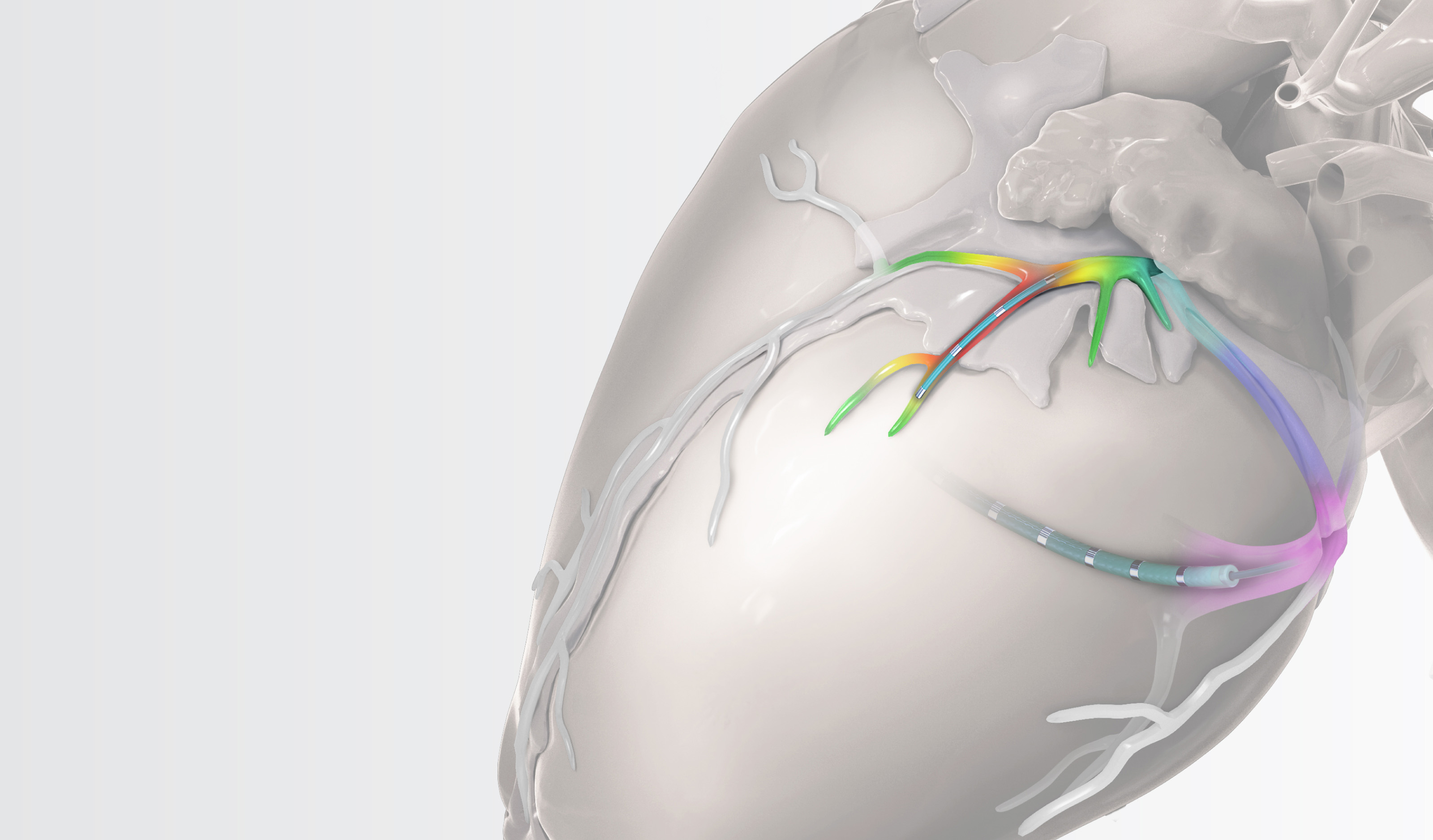
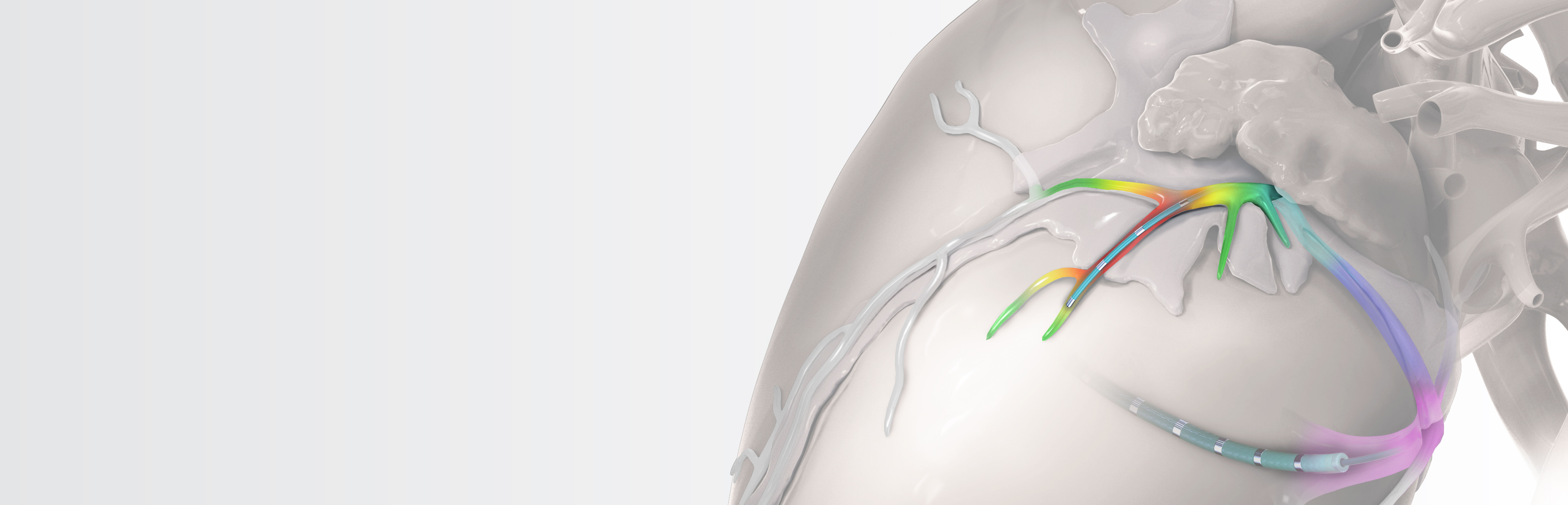
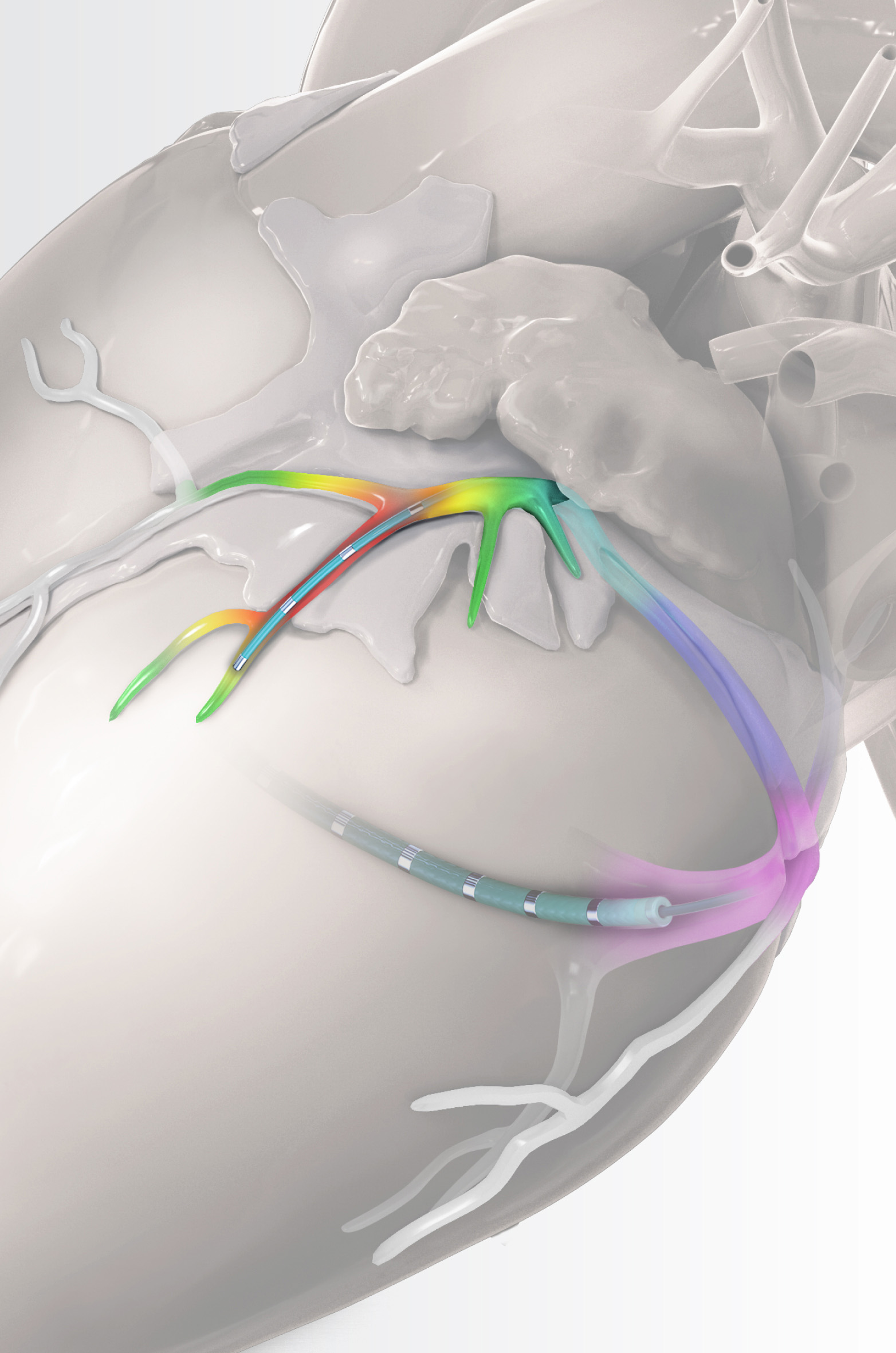
Complex Diagnostic Mapping Solutions
Go Further. Know More.™
Enhanced diagnostic precision for coronary sinus mapping and beyond.
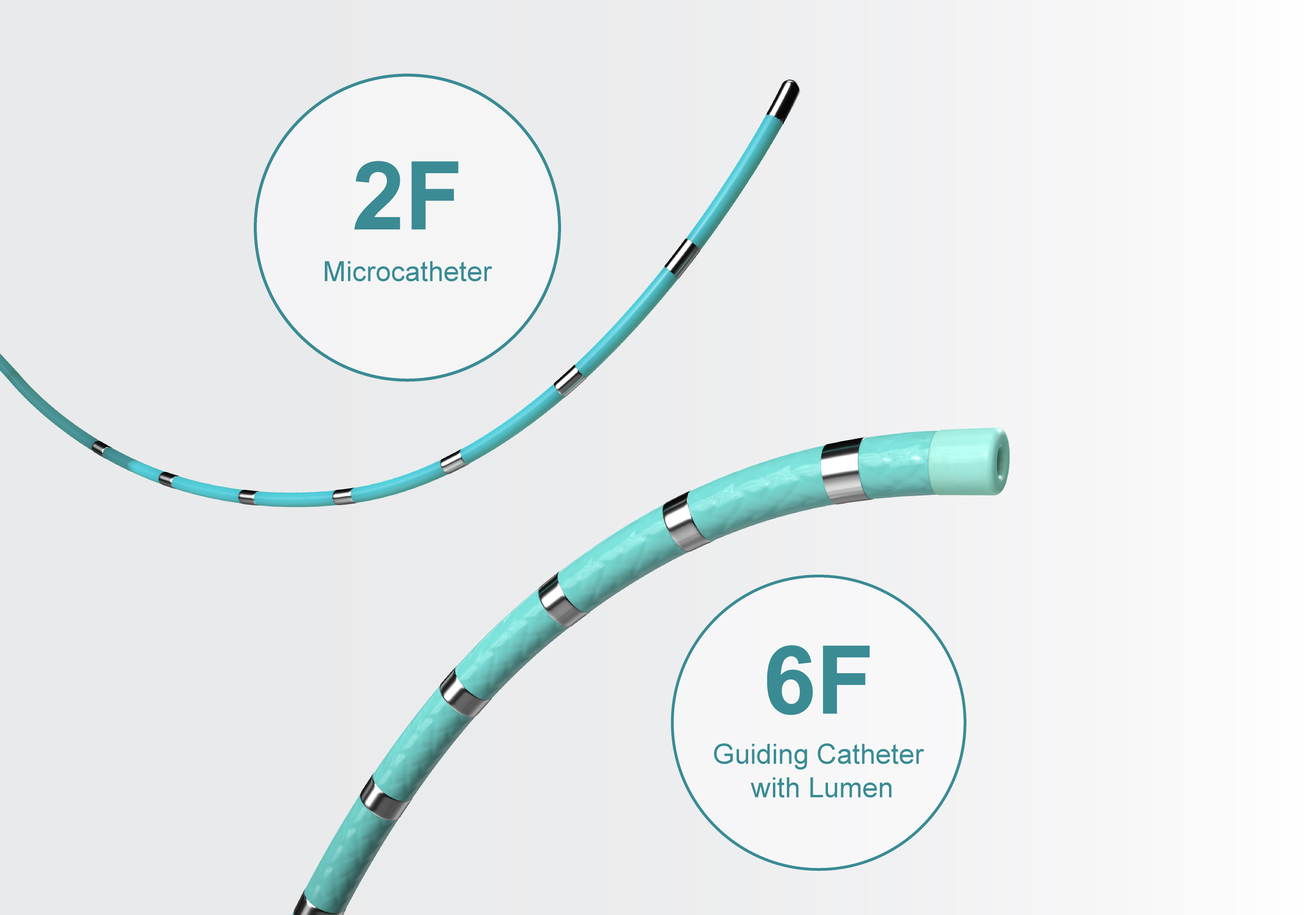

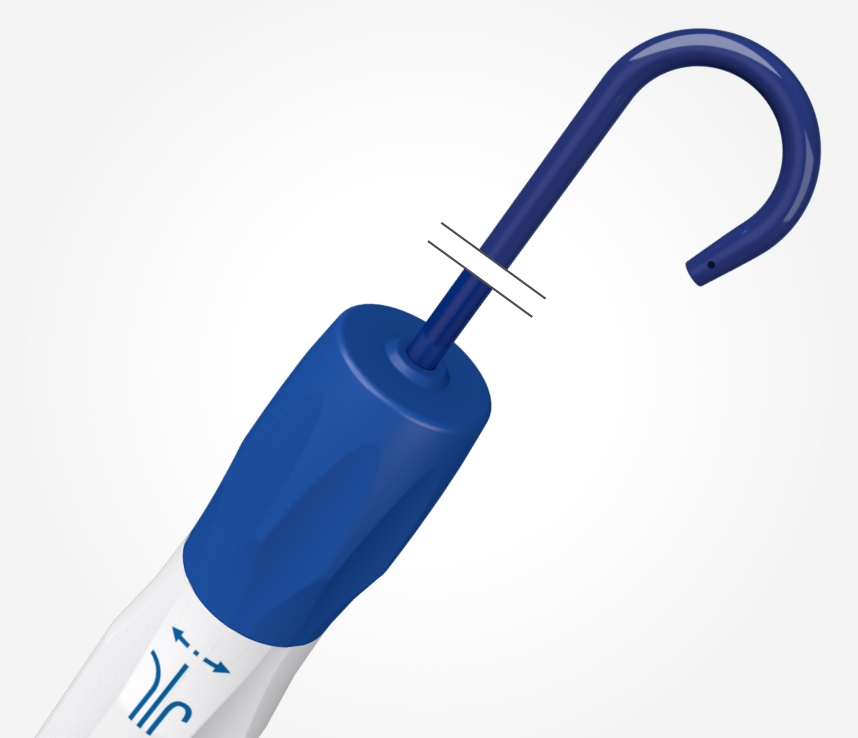
EPstar 2F Fixed Electrophysiology Catheter
The EPstar 2F microcatheter enables mapping and pacing in distal coronary sinus branches, inaccessible to other catheters.
EPstar 6F Fixed Electrophysiology Catheter with Lumen
The EPstar 6F catheter is an EP catheter capable of mapping in the CS. It is torquable with a large lumen, facilitating placement and telescoping of the 2F microcatheter in the coronary venous system.
Go Further. Know More.™
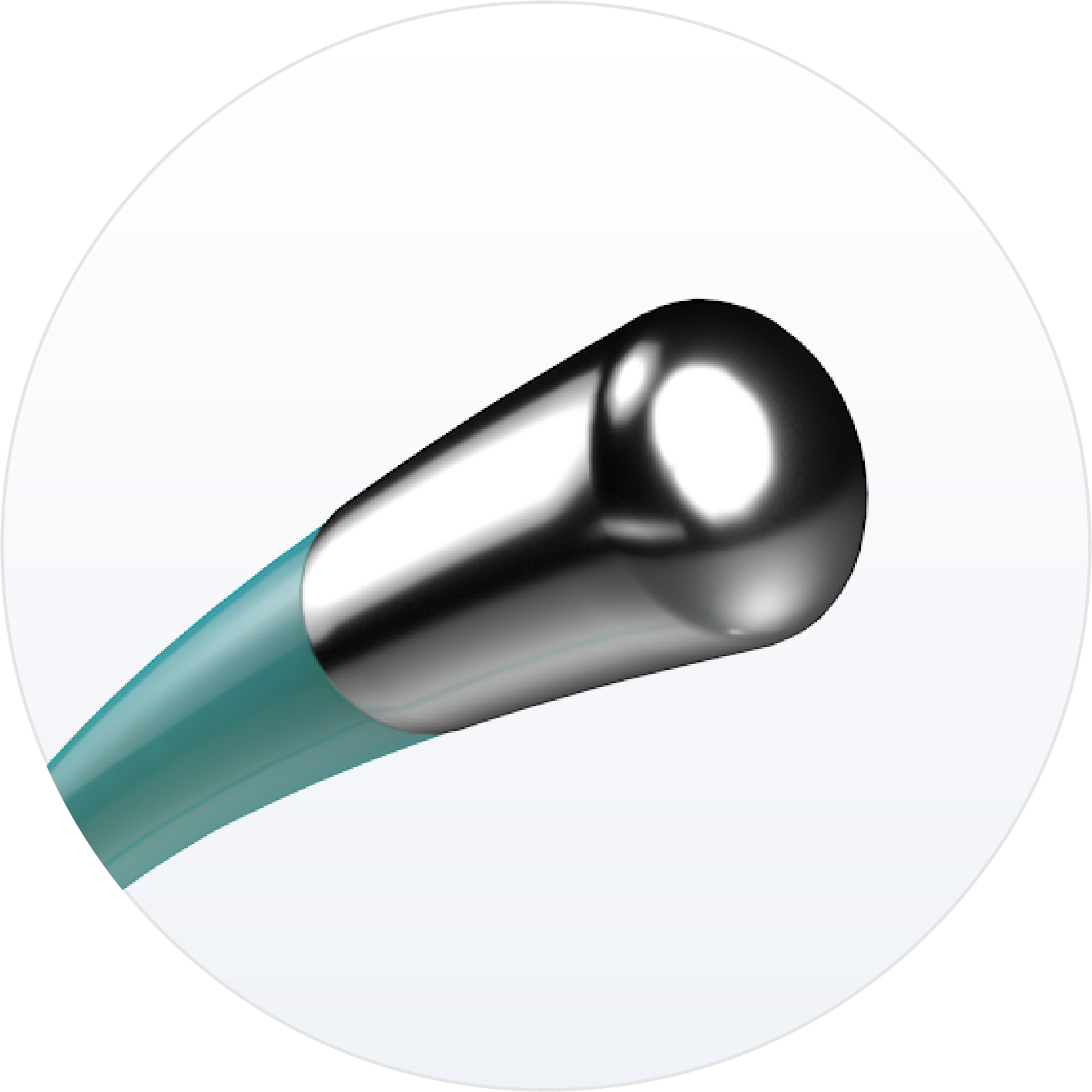

2F Confidence
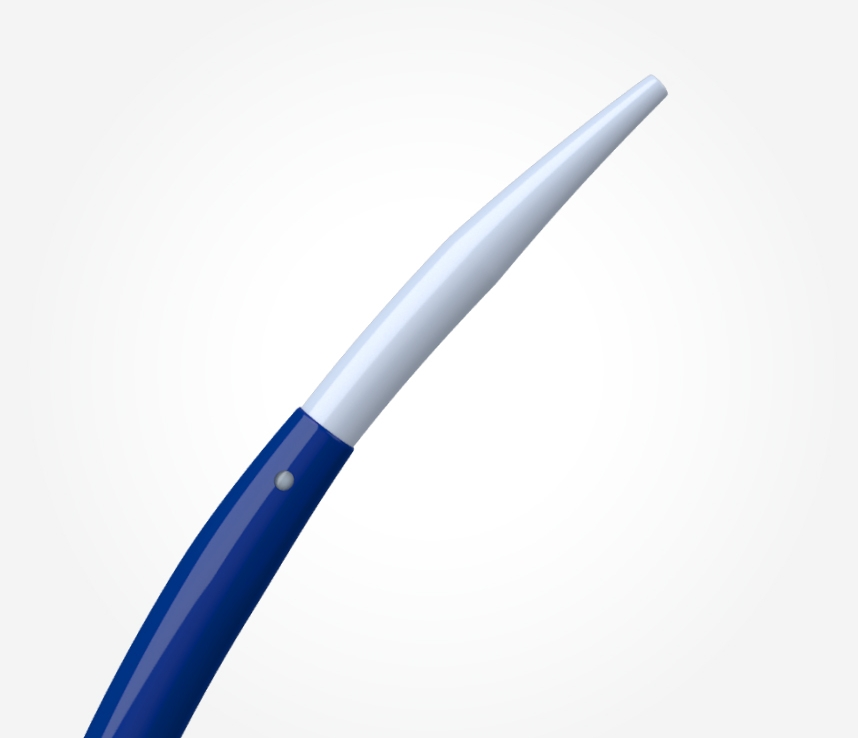
Atraumatic distal tip facilitates confidence in accessing branches of the CS.

2F Enhanced Pacing
Larger 1.5 mm and 1.3 mm electrodes for crisp electrograms and better pacing.

Broad Coverage
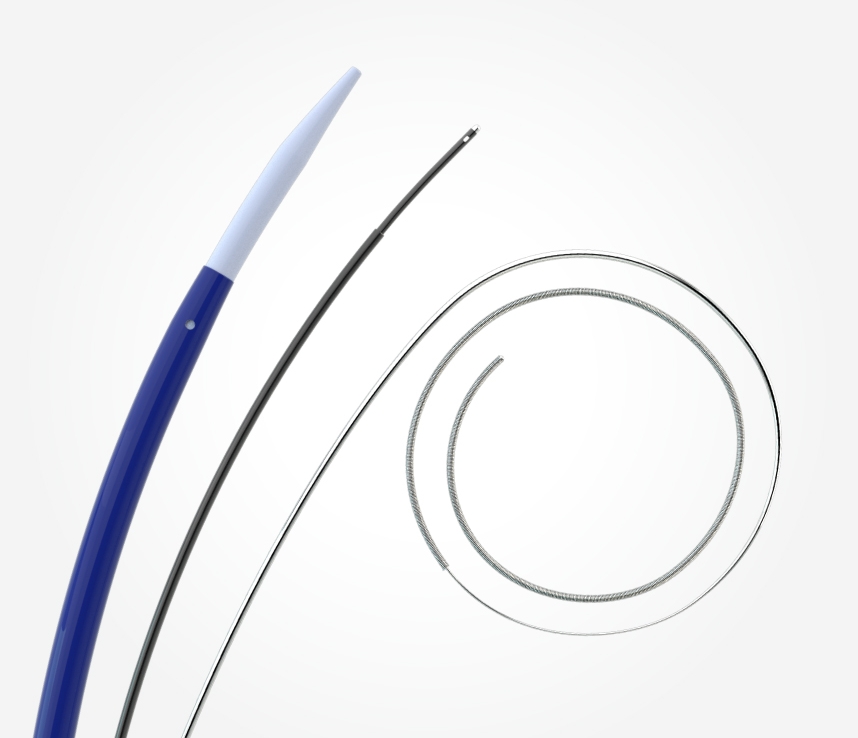
With the octapolar EPstar 2F and the decapolar EPstar 6F Catheter with Lumen, achieve optimal coverage for mapping with 18 electrodes total.
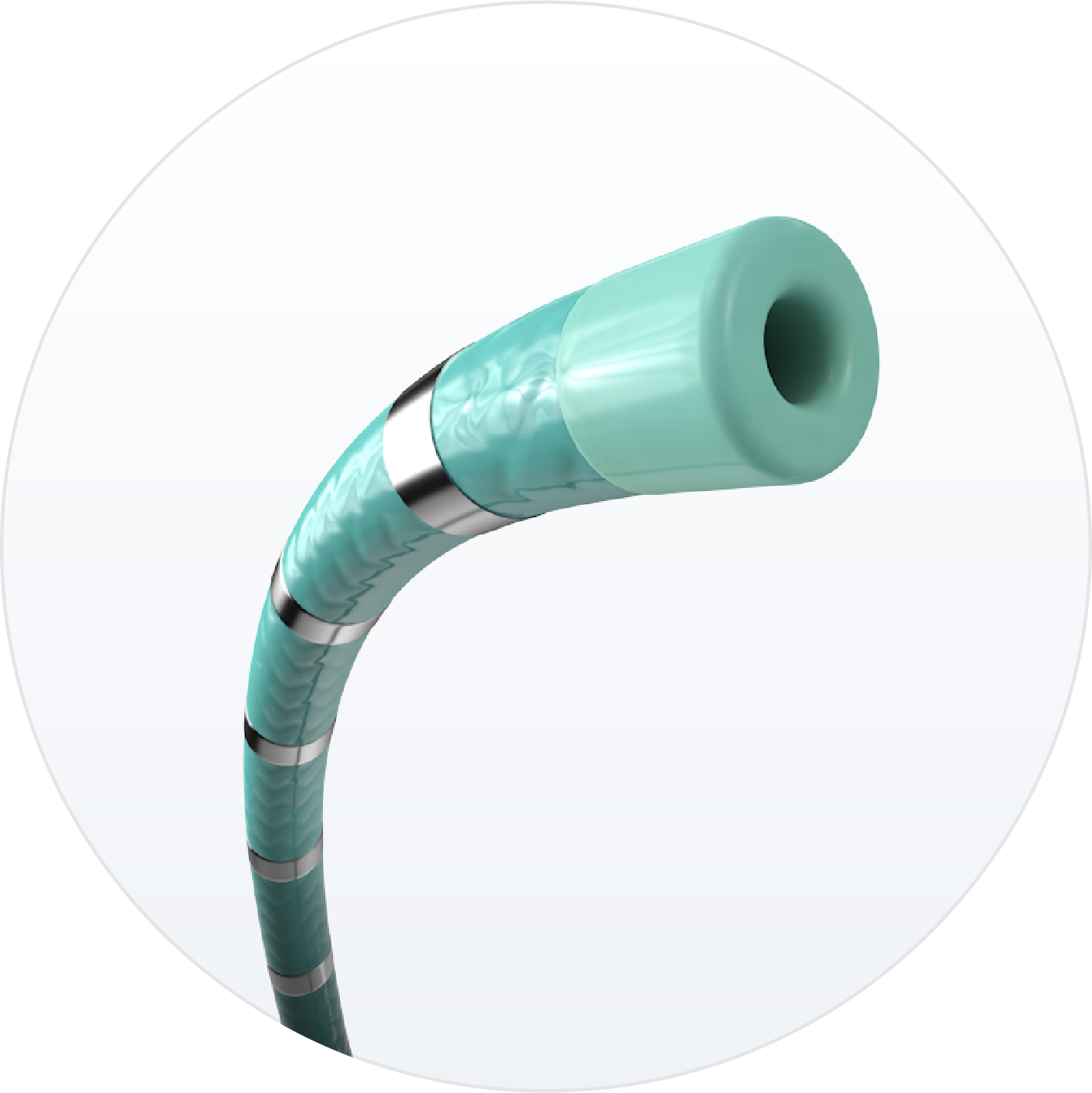

6F Soft Touch
Maneuver confidently in the CS: stiffness decreases gradually towards a soft distal tip.
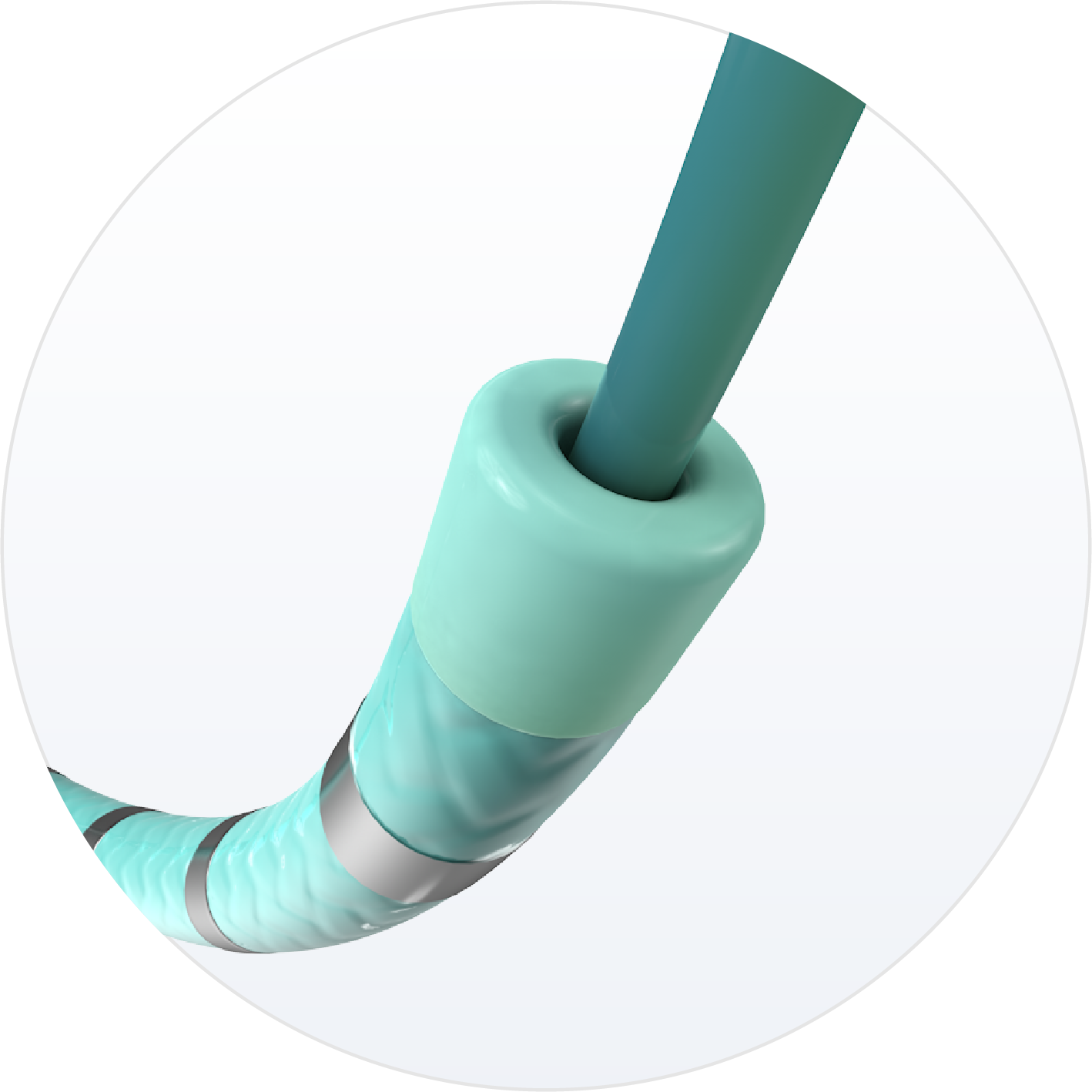

6F Wide Lumen
3F lumen allows for flushing and aspiration of fluids, and is compatible with devices up to 0.035” diameter.
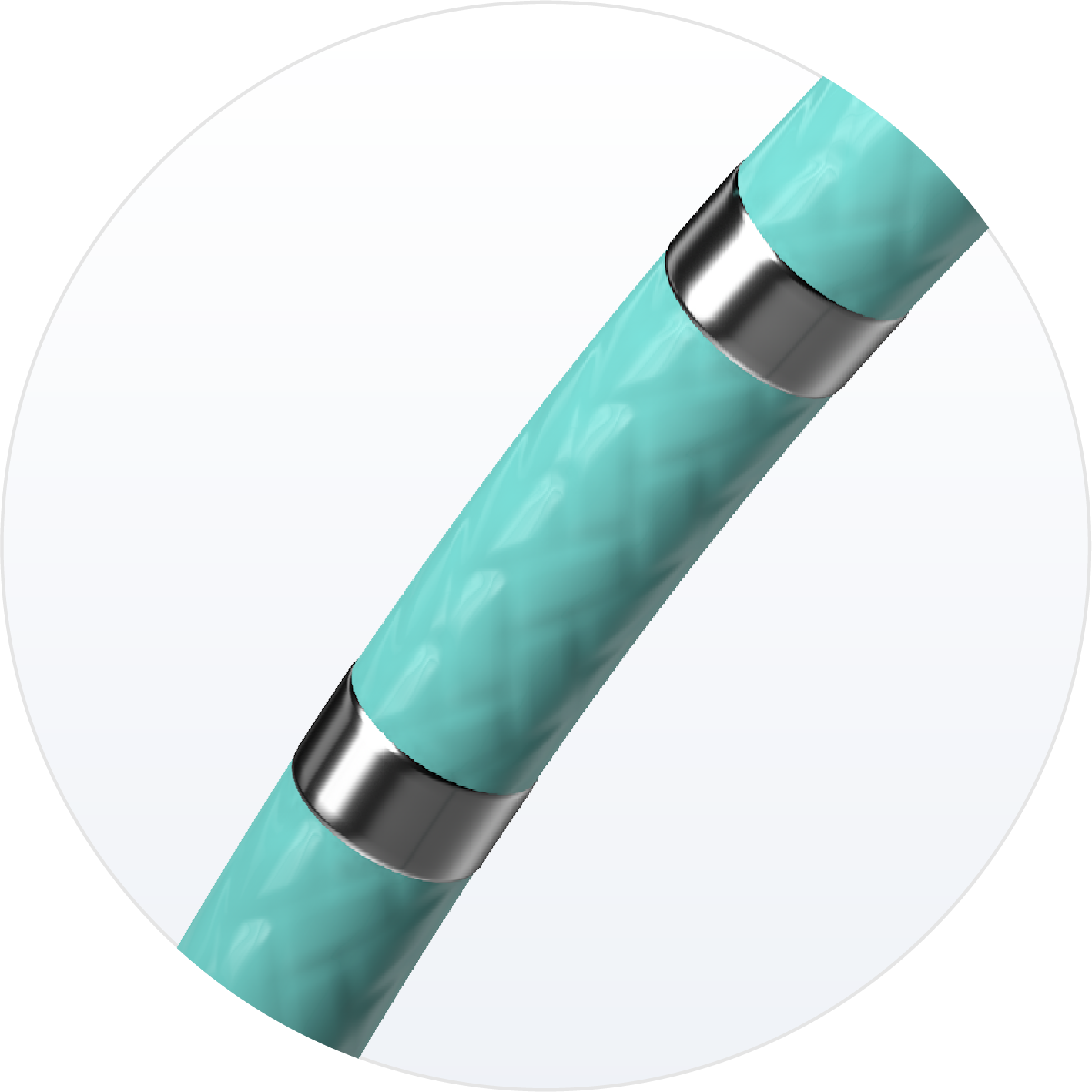

6F Control
Fully braided shaft, even under electrodes, allows greater maneuverability.
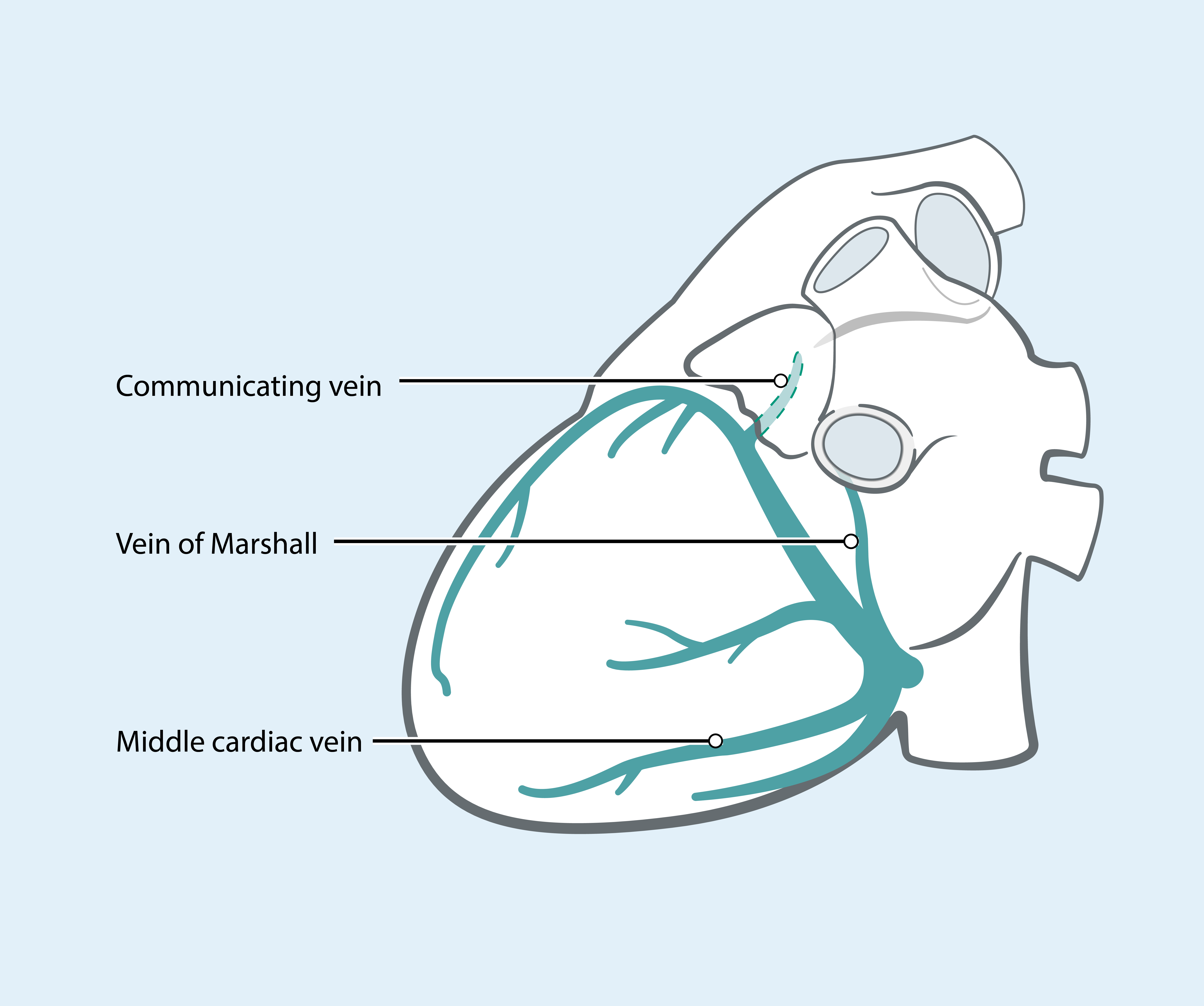
EPstar 2F Microcatheter
2F microcatheter may be deployed to map in the distal branches of the CS.
2F mapping has been used for:
- Idiopathic VTs1,2
- Complex ATs3,4
- Left WPW 5
- Mapping and pacing in VOM3,6
Evidence
Technical Specifications
EPstar Fixed Electrophysiology Catheter - 2F
| Feature | Specifications |
|---|---|
| French size | 2F |
| Electrodes |
8 Octapolar |
| Usable length | 130 cm |
| Electrode spacing | 5-5-5 mm |
| Electrode size |
1.3 mm Distal tip: 1.5 mm |
EPstar Fixed Electrophysiology Catheter with Lumen - 6F
| Feature | Specifications |
|---|---|
| French size | 6F |
| Electrodes | 10 (65 cm), 11 (95 cm) |
| Usable length | 65 cm, 95 cm |
| Electrode spacing |
5-5-5 mm, 2-8-2 mm (65 cm) 5-5-5 mm decapolar, additional indifferent electrode 220 mm from distal tip (95 cm) |
| Electrode size | 1.2 mm |
Ordering Information
| Product Type | Product | Electrode Spacing | Product Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Catheters | EPstar Fixed Electrophysiology Catheter - 2F |
5-5-5 mm |
DCF-2-8-55-130 |
| EPstar Fixed Electrophysiology Catheter - 6F (95 cm) | 5-5-5 mm | DLF-6-10-55-95R | |
| EPstar Fixed Electrophysiology Catheter - 6F (65 cm) | 5-5-5 mm 2-8-2 mm |
DLF-6-10-55-65 DLF-6-10-28-65 |
|
| Solution Kits | EPstar Coronary Venous Mapping Solution* | N/A | DLFK0007 |
| EPstar Bundle 6F kits (555) | N/A | DLK-2-55-6-55-65 | |
| EPstar Bundle 6F kits (282) | N/A | DLK-2-55-6-28-65 | |
| Cables | Electrophysiology Cable (10 pins, resterilizable - 5 uses) | N/A | DEX-10 |
| Electrophysiology Cable (14 pins, single use) | N/A | DEX-14 |
*Includes 6F 95 cm, and required cables.
Resource Library
Browse content specific to this product, such as brochures, publications, white papers, IFUs, videos and other product information.
BROWSE LIBRARY
Clinical Support
If you require an in-service training session or a follow up visit from one of our representatives, please contact us.
CONTACT SUPPORT
- Idiopathic Ventricular Arrhythmias Originating From the Vicinity of the Communicating Vein of Cardiac Venous Systems at the Left Ventricular Summit Komatsu Y, et al. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.117.005386
- Simultaneous Mapping in the Left Sinus of Valsalva and Coronary Venous System Predicts Successful Catheter Ablation from the Left Sinus of ValsalvaIto S, et al. PACE. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2005.00081.x
- Characteristics of Marshall bundle-related atrial tachycardias using an ultrahigh-resolution mapping system Kawamura I, et al. J Interv Card Elecr. doi: 10.1007/s10840-019-00544-9
- Marshall bundle reentry: A novel type of macroreentrant atrial tachycardiaYamamoto T, et al, Heart Rhythm. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2014.03.051
- Simultaneous mapping of the tricuspid and mitral valve annuli at electrophysiological studyDavis L, et al. Br Heart J. doi: 10.1136/hrt.73.4.377
- Importance of the vein of Marshall involvement in mitral isthmus ablationFujisawa T, et al. PACE. doi: 10.1111/pace.13640